Personal information represents a highly valuable asset for organizations today. It plays a crucial role in establishing strong relationships with clients and employees, fostering loyalty, and maximizing, customer lifetime value. When managing a resource as important as personal information, organizations must treat that data with the respect its owners (your clients and employees) deserve and the care and attention that increasingly stringent global privacy regulations (GDPR, CPRA, HIPPA, etc.) demand. Decentralized identity ushers in a new era of data security, safeguarding personal information for individuals and organizations while delivering substantial benefits for both parties.
Benefits of Decentralised Identity for the Individual
Decentralized identity empowers individuals by giving them the ability to participate in digital transactions and interactions on their own terms.. The benefits of decentralized identity for individuals include:
- DATA OWNERSHIP AND CONTROL
Individuals retain ownership and control over their personal data, deciding who can access and use it. - SELECTIVE DATA SHARING
Decentralized identity systems enable selective data sharing, preserving greater privacy by allowing individuals to share only necessary information with trusted organizations. - REDUCED DATA BREACH RISK
By reducing the need to share and validate data across multiple third-party organizations and international borders, decentralized identify reduces the risk of large-scale data breaches, identity theft, and fraud. - INTEROPERABILITY AND PORTABILITY
Individuals can use their decentralized identity across various applications and platforms, allowing for easy and secure data sharing between different services while improving user experience.
Benefits of Decentralized Identity for Organizations
Overall, decentralized identity empowers organizations with improved security, efficiency, and trust while enabling them to adapt to evolving privacy regulations and take advantage of emerging business models. Benefits include:
- ENHANCED DATA SECURITY
Organizations can securely store and manage valuable user data without becoming the central point of vulnerability, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. - STREAMLINED USER AUTHENTICATION
Decentralized identity enables seamless and efficient user authentication processes, eliminating the need for complex and cumbersome registration systems. This improves user experience and reduces friction. - COST SAVINGS
Implementing decentralized identity can lead to cost savings by reducing infrastructure and maintenance expenses associated with traditional identity management systems. - COMPLIANCE AND REGULATORY ALIGNMENT
Decentralized identity solutions can help organizations comply with data protection regulations, as they provide individuals with more control over their data and consent management. - TRUST AND REPUTATION
By adopting decentralized identity, organizations can enhance their reputation and build user trust. The transparent and secure nature of decentralized identity systems fosters trust in data handling practices. - INTEROPERABILITY AND PORTABILITY
Decentralized identity enables seamless interoperability between different organizations and platforms, facilitating secure data sharing and collaboration. - BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES
Embracing decentralized identity opens up new business opportunities, such as offering personalized services, creating trust networks, or participating in decentralized ecosystems.
The High Cost of Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns
While the benefits of decentralized identity speak for themselves, we should always maintain sight of the risks associated with managing personal information. Never forget personal information is a prime target for malicious individuals seeking unauthorized access to exploit personal data for their own gain, and the cost of these breaches can be significant.
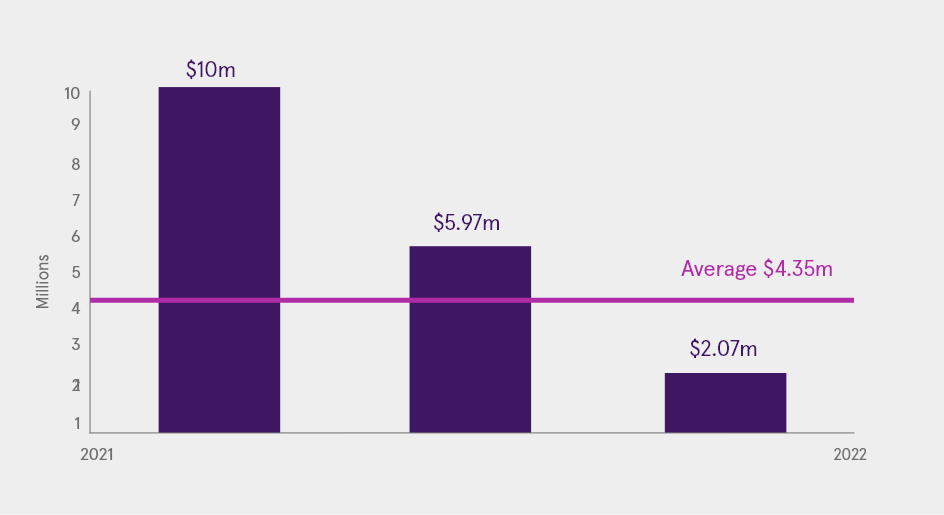
- In 2022, the global average data breach cost was $4.35 million.
- Between March 2021 and March 2022, healthcare organizations incurred an average cost exceeding $10 million due to data breaches. In that same time frame, data breaches cost financial institutions an average of $5.97 million and public sector organizations an average of $2.07 million.
- Under the EU’s GDPR, the maximum fine for severe data breaches is up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual revenue (whichever is higher). The cumulative sum of GDPR fines issued between July 2019 and December 2022 was €2,4 million.
- Research by the IAPP suggests that 68% of global consumers are concerned about their online privacy. These concerns can lead to friction during the registration process leading to less-than-optimized client acquisition and onboarding.
Decentralized identity mitigates these risks and protects organizations and individuals from the potentially devastating financial and reputational consequences of data breaches.
How is Decentralized Identity Different from Traditional Systems?
In traditional identity systems, personal information is typically stored in centralized databases and controlled by third parties. This creates concerns regarding data breaches, privacy violations, and limited control over personal information. Decentralized identity aims to address these issues by shifting the control of identity data back to the individuals themselves.
Decentralized identity systems enable individuals to retain ownership and control over their identity attributes. Moreover, decentralized identity systems allow users to selectively disclose their identity information, sharing only the necessary attributes required for a particular transaction or interaction. This enhances privacy by mimizing the exposure of personal data. It also enables users to maintain multiple identities for different contexts, improving security and reducing the risk of identity theft or impersonation.
How Does Decentralized Identity Work?
The field of decentralized identity is undergoing rapid evolution, necessitating specialized technical approaches and architectures tailored to specific projects and initiatives. Nonetheless, the following points provide a concise overview of the typical operational framework of a decentralized identity system.
- DECENTRALISED IDENTIFIERS (DIDs)
DIDs are unique identifiers that form the basis of decentralized identity. DIDs are typically represented as strings of characters, such as URLs, and serve as a way to locate and identify specific individuals or entities in the decentralized identity system. DIDs are like unique addresses associated with individuals or entities. DIDs can be created by individuals themselves or given by trusted entities. - DID DOCUMENTS
Each DID is accompanied by a DID document containing information about the associated entity. This document provides public keys and other details that allow others to verify and authenticate the identity of the entity linked to the DID. - VERIFIABLE CREDENTIALS
Verifiable credentials are verifiable pieces of information associated with a DID, such as educational degrees, certifications, or personal attributes. These credentials are issued by trusted parties like schools, government agencies, or employers and are often digitally signed to ensure they are genuine and haven’t been tampered with. - SELECTIVE DISCLOSURE AND CONSENT
One of the advantages of decentralized identity is that individuals have complete control over their personal data. They can choose which identity attributes to disclose in different situations, providing only the necessary information without revealing their complete identity or personal details. This approach safeguards privacy and limits the exposure of sensitive information. - AUTHENTICATION AND VERIFICATION
Authentication and verification in a decentralized identity system involves relying parties (such as a service provider or an application) verifying the signatures on the DID documents and verifiable credentials. By checking the signatures against the corresponding public keys stored in the DID documents, these parties can confirm the information’s authenticity and integrity. - INTEROPERABILITY AND STANDARDS
Interoperability is crucial for decentralized identity systems to work seamlessly across different platforms and services. To achieve this, open standards and protocols are developed and adopted. These standards ensure compatibility and enable different decentralized identity systems to work together, allowing individuals to use their DIDs and verifiable credentials across various contexts and environments.
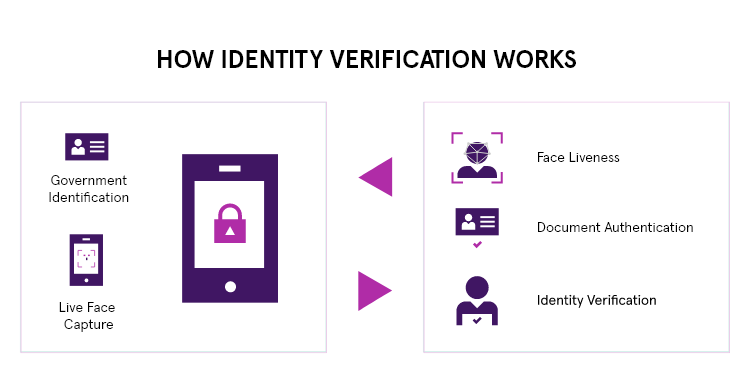
The Role of Digital Wallets in Decentralized Identity
Digital wallets play an essential role in decentralized identity systems by providing a secure and user-friendly way for individuals to manage and interact with decentralized identities.
Digital wallets act as a repository for storing and managing DIDs associated with an individual. The wallet keeps track of the user’s DIDs and provides easy access for their use in various identity-related interactions.
Digital wallets also enable the storage and management of verifiable credentials associated with a user’s decentralized identity. Users can receive, view, and store their verifiable credentials, such as educational degrees, certifications, or personal attributes, within their wallets. The wallet then provides an interface for users to organise and selectively present these credentials when needed.
What Kind of Organization Will Benefit from Decentralized Identity?
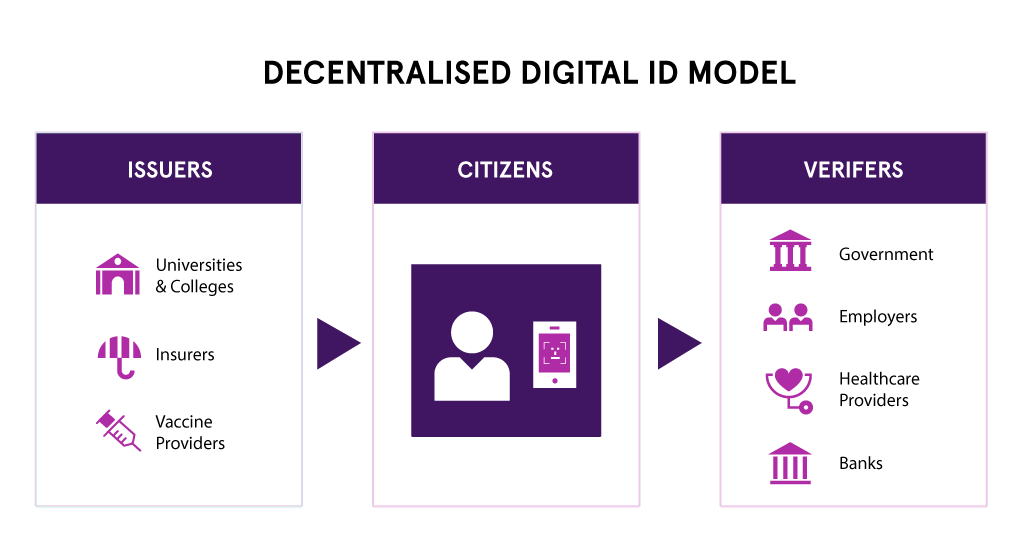
A wide range of organizations across various industries and sectors will benefit from deploying decentralized identity. These include:
- FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions can benefit from decentralized identity by enhancing customer onboarding processes, streamlining Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, and improving identity verification for digital transactions. Decentralized identity can help reduce fraud, enhance security, and provide customers with a more seamless and convenient user experience. - HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
Healthcare organizations, including hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies, can benefit from decentralized identity to improve patient identity management, secure health records, and enable the secure sharing of medical information across different healthcare providers. Decentralized identity can enhance data privacy, facilitate interoperability, and empower patients to have greater control over their health data. - GOVERNMENT AGENCIES
Government entities can leverage decentralized identity to enhance citizen services, streamline identity verification for public services, and improve the security and integrity of personal data. Decentralized identity can enable secure and tamper-proof identity credentials, facilitate cross-agency data sharing, and enhance citizen trust in government services. - EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS
Schools, colleges, and universities can benefit from decentralized identity for student identity management, secure issuance of verifiable credentials, and streamlined verification of academic achievements. Decentralized identity can enable verifiable and tamper-proof educational records, simplify credential sharing with employers or other institutions, and provide individuals with greater control over their academic achievements. - ECOMMERCE AND RETAIL
Online retailers and e-commerce platforms can leverage decentralized identity to enhance customer trust, enable frictionless user experiences, and combat fraud. Decentralized identity can improve user authentication, facilitate secure and personalized customer interactions, and enable the seamless sharing of verified customer attributes across different e-commerce platforms.
Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) and Decentralized Identity
Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) solutions increasingly incorporate decentralized identity to provide seamless and secure experiences for all customers while managing customer identities at scale.
DIDs and verifiable credentials issued within a decentralized identity system can be utilised by CIAM systems to verify and authenticate customer identities in a more robust and privacy-preserving manner. This enhances security, reduces reliance on centralized identity repositories, and helps prevent identity fraud.
IN SUMMARY
Decentralized identity represents a paradigm shift towards empowering individuals with greater control, privacy, and security over their digital identities in an increasingly interconnected and data-driven world.
To learn more about how ProofID can help your organization create a more secure environment for its clients and employees’ personal information, reducing risk, and improving user experience, contact us to speak with one of our decentralized identity experts.
Be the first to hear about news, product updates, and innovation from proofid








